[ad_1]
Most analysts and economists had forecast that the central bank would increase rates by 25 basis points on Thursday.
Announcing the unanimous decision of the six-member committee on Thursday, RBI governor Shaktikanta Das said that the MPC decided to wait for the impact of the earlier rate hikes to play through the economy. “This is a pause and not a pivot,” said Das, adding that the MPC would be in readiness to act should the situation so warrant.
While the repo rate — the rate at which RBI lends to banks – remains unchanged at 6.5%, the cost of wholesale borrowings in money markets could rise for banks and corporates. This is because of the RBI’s decision to reduce surplus liquidity.
While home loan rates are linked to the repo, a significant portion of corporate loans are linked to the bank’s cost of funds, which includes money market rates. Also, large corporates raise short-term funds through the issue of three-month commercial paper, which will become costlier.
According to Saugata Bhattacharya, chief economist, Axis Bank, the decision to pause was a reflection of the extreme uncertainty which characterises the global economy and the risks of its potential spillovers into India.
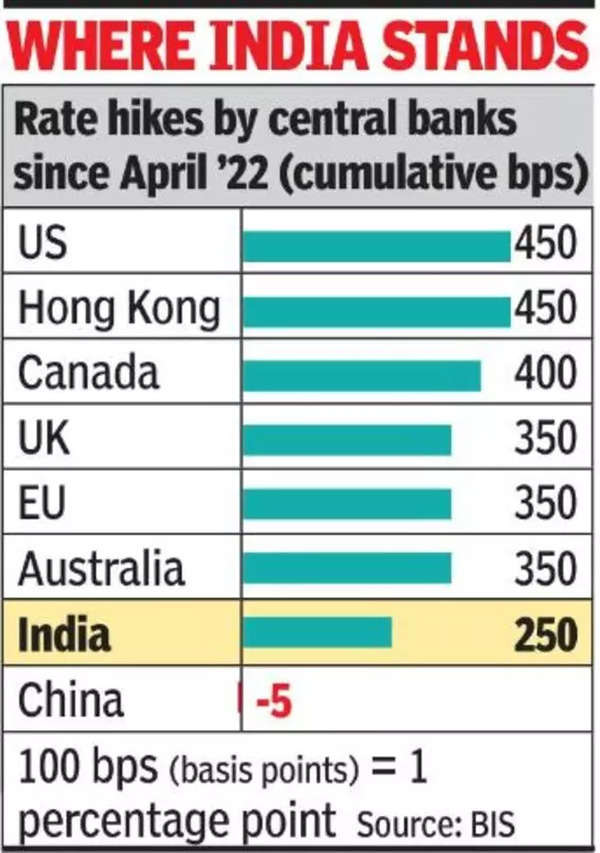
Five of the six-member rate-setting committee voted in favour of continuing to withdraw liquidity from the money markets as inflation continued to remain high. This is the first pause since the RBI began its current rate hiking cycle, which began in May 2022 and comprised six rate hikes, which took the repo rate up by a cumulative 250 basis points.
The RBI has forecast inflation at 5.2% in 2023-24, and GDP growth at 6.5% in the current financial year.
The RBI’s rate hike is contrary to the decisions of the US Federal Open Market Committee and the Bank of England, both of which raised interest rates recently, but in line with the Reserve Bank of Australia, which voted for a pause. While some economists had said that the RBI may choose to pause and wait for the impact of earlier rate actions, the majority view was that the central bank would increase rates in view of firming crude oil prices.
Announcing the MPC’s decision, Das said that while 2023 started on a positive note, the narrative changed within weeks with the banking crisis in the US. He described as unprecedented the uncertainty in geopolitics and financial markets.
Das also pointed out to the introduction of the standing deposit facility last year, which effectively raised the RBI’s borrowing rate from banks by 40 basis points, as part of the rate hike. Das said that considering the standing deposit facility, the total rate hikes since May 2022 worked out to 290 basis points.
While the MPC members were unanimous in voting for a pause, external member Jayanth Varma was the sole dissenter against the proposal to withdraw accommodation.
[ad_2]
Source link
